CEM researchers are studying the metabolism and water-oxidizing capabilities of cable bacteria to develop more efficient methods of CO2 reduction. The group have dicovered a novel mechanism in cable bacteria for H2O oxidation in the conductive fibers from the cells’ periplasms. They are studying whether this novel mechanism could inspire a new type of biomimetic catalysts for use in CO2 reduction technologies.
Their project aims to investigate how this reaction works in cable bacteria by analyzing the protein structure and function of the catalytic water-splitting site.
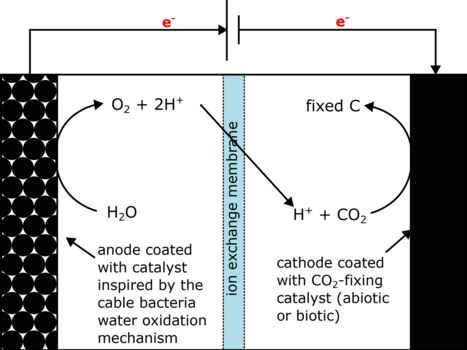
The CEM researchers study the newly discovered cable bacteria, which in chains form centimeter long electrical wires. By doing so the cable bacteria can connect various biochemical processes with electric currents and are a particularly prominent example of the rapidly growing research field of electromicrobiology. CEM is located at Aarhus University, Section for Microbiology and combines expertise in the application and development of methods in microbiology, molecular biology, electrochemistry, measuring technology and nanoscience.
Center for Electromicrobiology, Aarhus University: Cable bacteria research (au.dk)
The Novo Nordisk Foundation CO2 Research Center is a mission‐oriented center with the purpose to develop novel science for CO2 capture and CO2 conversions for storage or utilization to replace fossil carbon and fossil fuel‐intensive processes with sustainable, CO2‐based technologies.
The Novo Nordisk Foundation CO2 Research Center - CORC (au.dk)